
As ETS may well provide the reference standard to assess the ROM of the musculoskeletal system in a clinical setting, concurrent use of ETS and simple two-dimensional measurement devices is a possible method to determine the validity of goniometers to yield plausible and useful objective ROM data. Electromagnetic tracking systems (ETS) enable the direct measurement of a three-dimensional position and the orientation of multiple sensors referred to a stationary source (transmitter). Three-dimensional measurement tools based on electromagnetic tracking have recently been used to precisely measure shoulder and spine ROM, as well as patellofemoral and hip joint kinematics. Elson and Aspinall proposed a new method for measuring range of hip flexion by palpating the lumbosacral junction to allow early identification of lumbar spine flexion which accompanies hip flexion. showed that in the hip flexion movement, as measured in a clinical setting, more than a quarter of the ROM can be attributed to pelvic tilt, leading to an immense misinterpretation of this movement due to the insensitivity of manual goniometers for secondary pelvic movement. The validity (i.e., the degree to which a measurement actually measures what it claims to measure) and reliability (i.e., the degree to which a measurement is consistent and stable) of manual goniometers have therefore been questioned, especially for measuring hip flexion. In addition, manual goniometers assess joint flexibility only in two dimensions however, as most of the hip ROM measures in clinical practice are practically in-plane movements, this limitation is minor. There are also difficulties in monitoring joints that are surrounded by large amounts of soft tissue, such as the hip. Major drawbacks of goniometry are that the starting position, the center of rotation, the long axis of the limb and the true vertical and horizontal positions can only be visually estimated moreover, conventional goniometers must be held with two hands, leaving neither hand free for stabilization of the body or the proximal part of the joint.
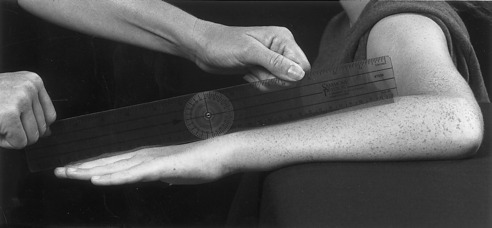
The two-arm goniometer is still the most commonly used, economical and portable device for the evaluation of ROM, despite acknowledged limitations. The advantages of goniometry are the simplicity in assessing ROM, the direct measurement of joint angles without any data reduction process and the low cost of the instrument. Hip joint ROM is widely assessed using low-technology tools such as manual goniometers or inclinometers. Hip joint range of motion (ROM) is a basic clinical parameter for diagnosing hip diseases, such as osteoarthritis or femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), and for monitoring the efficacy of a treatment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
